Blog
News
Kazakhstan Driver License Knowledge Test Integrity Case Study
How Kazakhstan secured driver license knowledge tests with an evidence-based exam integrity stack: seat-level identity checks, secure workstations, device/VM detection, audit trails, and fair appeals workflows.
Nurali Sarbakysh
CEO
Jan 8, 2026

I am Nurali, CEO at TrustExam.ai. Over the last six years I have worked with education and government teams on exam integrity in regulated, high-volume programs. Driver license knowledge testing in Kazakhstan taught a clear lesson: integrity is not a single control. It is a system of evidence, operations, and governance that must survive audits and public scrutiny. This case study shares the threat model we used, the detection layers that mattered, and a rollout playbook you can adapt.
Problem statement: when a theory test loses credibility, the whole licensing system suffers
A driver license knowledge test is a public safety gate. It is also a social trust contract. If candidates believe results can be bought, compliance drops. Honest candidates disengage. Audit bodies react. The testing operator becomes a political target. The challenge is scale: theory tests run across many centers with staff rotation and uneven infrastructure.
In Kazakhstan, the goal was not perfect prevention. The goal was fewer easy bypass paths, stronger evidence, and consistent decisions during reviews and appeals.
Threat model for driver license knowledge tests
Most fraud schemes fit three patterns. Impersonation and substitution: a proxy candidate sits the test for someone else. Covert assistance: a candidate receives answers via micro-earpiece, hidden camera, or a helper outside the room. Workstation bypass: remote access tools, virtualization, screen mirroring, or unauthorized peripherals expose external help.

Detection and prevention layers that worked as a stack
Results improved when we treated integrity as a stack. Each layer blocks a different bypass path. The stack also correlates signals into an evidence packet that reviewers and auditors understand.
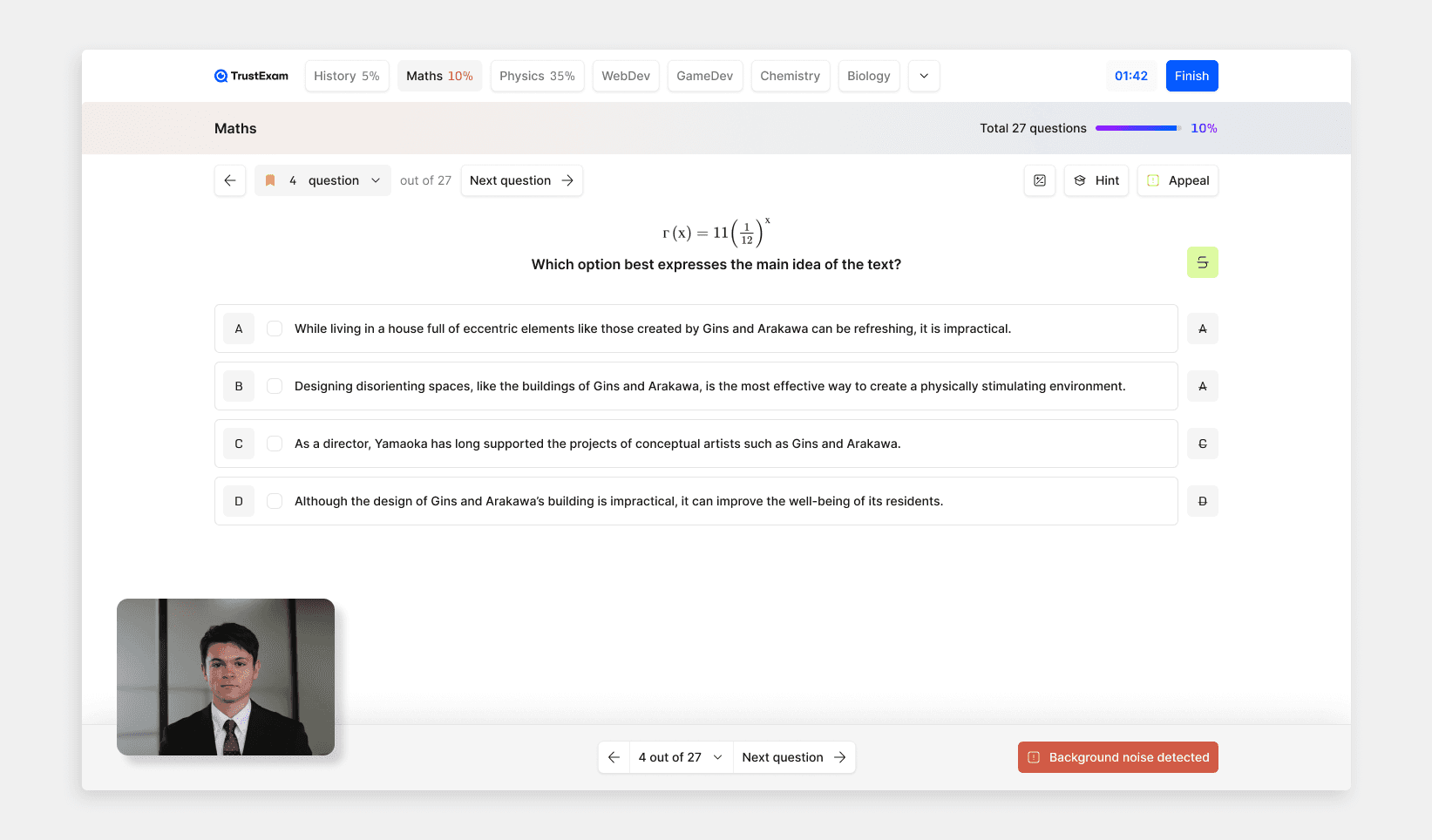
Layer 1: seat-level identity assurance
Identity checks at the entrance are necessary, but not sufficient. The control point is the exam seat. We combined document checks with biometric verification and continuity checks during the session. This reduces substitution attempts and creates a baseline for investigation.
Expert Tip
"Treat identity as a continuous process, not a one-time gate. If outcomes must be defensible, build continuity at the seat and log it."
If your agency is exploring identity assurance for licensing exams, start with an integrity risk assessment and a pilot plan. The TrustExam.ai online proctoring platform supports identity checks, reviewer workflows, and audit-friendly evidence timelines. TrustExam.ai online proctoring platform: https://trustexam.ai
Layer 2: secure workstation and device integrity controls
In licensing tests, many attacks look like normal computer use. A secure browser alone is not enough. Controls should harden the workstation profile and monitor for known bypass classes: virtual machines, remote desktop tools, virtual camera feeds, unauthorized peripherals, and screen mirroring paths such as HDMI splitters. Standardization matters too. A common workstation profile reduces variance across centers and supports fairness.
Layer 3: detection of covert assistance and collusion
Covert assistance needs triage, not automatic punishment. Audio anomalies, behavior shifts, and timing patterns are useful when they trigger targeted review. Correlation is key. One signal can be noise. Multiple signals in the same time window warrant human review.
Layer 4: evidence packets for review and appeals
Detection without governance creates conflict. Reviewers need consistent evidence. Appeals teams need a repeatable format. We framed every flagged case as an evidence packet: a timeline of events, supporting signals, and reviewer notes. This reduces subjectivity and speeds up dispute handling.
Comparison table
Method | Evidence strength | Cost | Scalability |
Room CCTV only | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Manual invigilators only | Medium | High | Low |
Seat-level identity checks only | Medium | Medium | High |
Secure workstation controls only | High | Medium | High |
Stack: identity + workstation + evidence timeline | High | Medium | High |
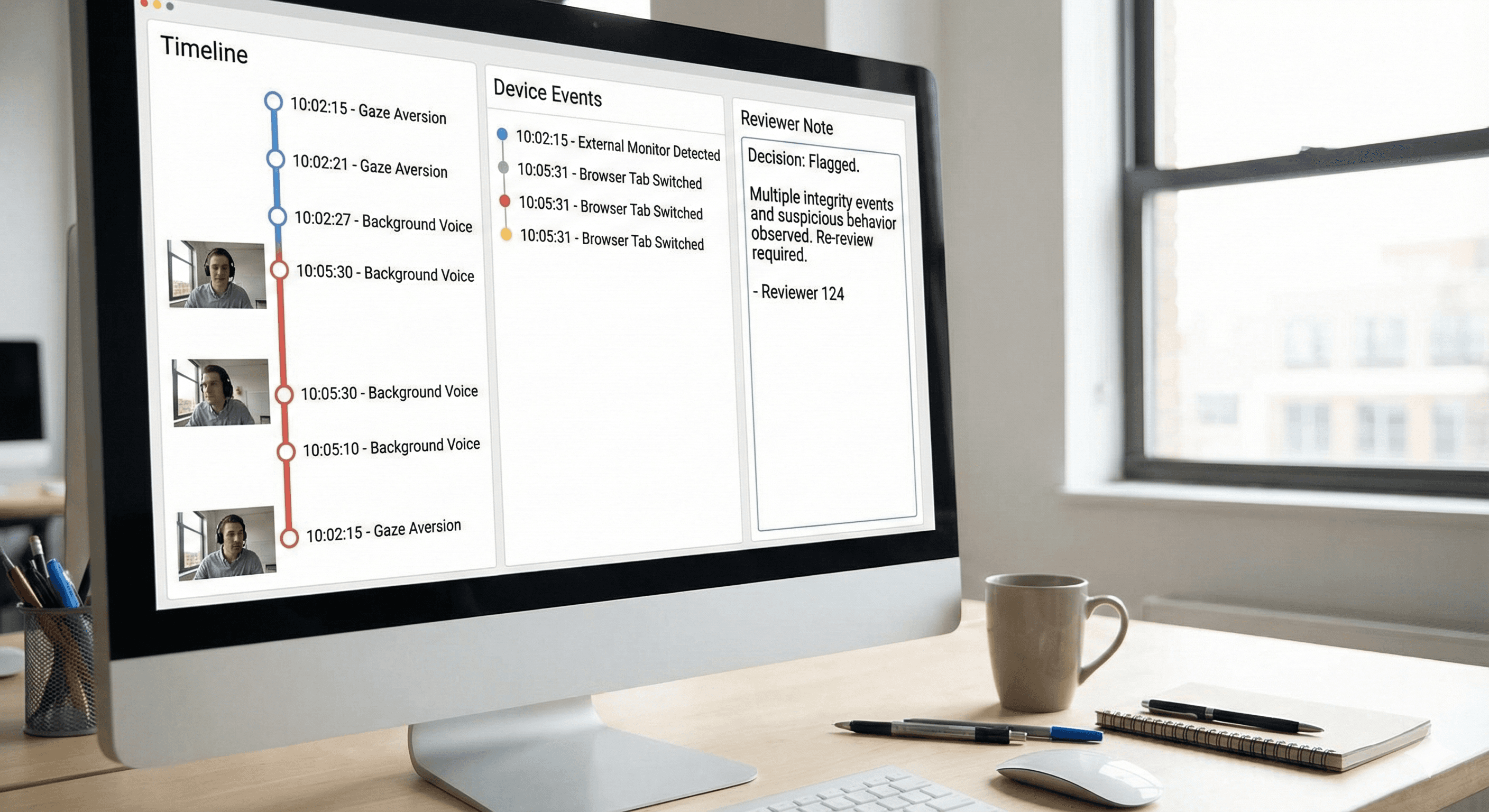
Implementation playbook: from pilot to national rollout
A driver license testing program is an operations project first. The biggest risk is inconsistent adoption across centers. We started with a pilot in a limited number of sites and defined measurable outcomes. We tested staff workflows, not only detection accuracy.
Before scaling, we standardized three assets: a workstation security baseline, a reviewer SOP, and a governance pack. The governance pack included the privacy notice, retention schedule, and role-based access policy.
Checklist table
Step | Owner | Deliverable |
Threat scenarios and thresholds | Exam authority + audit | Integrity rules document |
Privacy notice and retention policy | Legal + security | Governance pack |
Workstation lockdown baseline | IT + center ops | Standard workstation profile |
Identity verification workflow | Operations | Seat-level identity SOP |
Reviewer workflow and evidence format | QA + audit | Review SOP and templates |
Pilot and KPI baseline | Program lead | Pilot report and metrics |
Scale and quality audits | Operations + audit | Training plan and QA cadence |
Expert Tip
"Do not scale until reviewers explain decisions with the same wording in every region. Consistency is a control."
Commercial insert
If you need an integrity stack designed for regulated exams, focus on auditability and operational scale. TrustExam.ai works with public sector teams on evidence-based reporting, reviewer workflows, and secure workstation controls for national programs. Proctoring for government exams: https://trustexam.ai/who-we-help/government
Governance: privacy, fairness, and human oversight
Integrity controls must respect privacy and due process. We recommend: data minimization, a retention schedule aligned to appeal windows, role-based access, immutable audit logs, and human-in-the-loop decisions for sanctions. Monitor regional variance and false positives.
For framing, NIST Digital Identity Guidelines help define assurance concepts. ISO/IEC 27001 helps structure security management expectations for vendors. ISO/IEC 30107-3 is useful when biometric liveness and presentation attack detection are in scope.
Measuring success without unrealistic claims
Track percent of sessions flagged for review, reviewer workload per 1,000 exams, appeals volume and resolution time, throughput per seat per day, and variance across centers. The objective is not perfection. The objective is fewer easy bypass paths and stronger evidence.
If you are benchmarking vendors, request a demo that shows the evidence packet and reviewer workflow, not just live monitoring. TrustExam.ai can share a licensing exam pilot blueprint and a procurement checklist based on large-scale deployments. AI online proctoring: https://trustexam.ai/online-proctoring
Conclusion
The Kazakhstan driver license knowledge test case reinforced a pattern we see globally. Integrity succeeds when it is treated as a system: seat-level identity assurance, secure workstation controls, signal correlation, and an audit-ready review process. The fastest way to start is a scoped pilot with clear KPIs and a governance pack that procurement and auditors can approve.
FAQ
1) What is the first control to implement in a testing center?
Seat-level identity assurance, supported by logs, plus a standardized workstation lockdown baseline.
2) Can CCTV replace an integrity platform?
CCTV is useful context. It rarely provides evidence strong enough for consistent appeals handling.
3) How do we reduce candidate friction while improving integrity?
Use risk-based review. Apply strict checks only when signals correlate and thresholds are met.
4) What makes an exam integrity decision defensible in audits?
A consistent evidence packet, a reviewer SOP, role-based access, and a documented appeals process.
Nurali Sarbakysh
CEO
Share